
By Dr Tejinder Kaur
AUB is a gynaecological condition marked by menstrual bleeding of abnormal quantity, duration or schedule. It impacts 1 in 5 women at some point in their life.
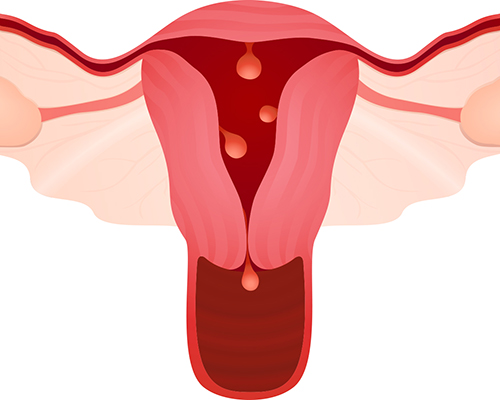
AUB is when bleeding is heavier or lighter than usual. It may be longer than expected, may occur early or late than the scheduled time, may occur at an irregular interval or randomly.
An average adult menstrual cycle is 21-35 days apart, and a normal teen menstrual cycle is 21-45 days apart. A normal menstrual flow lasts from 3-7 days with a blood loss between 5-80ml (i.e., changing one pad/day to 3/day). Any deviation from normalcy is considered abnormal and should be investigated.
Bleeding does NOT occur during pregnancy and once a woman has attained menopause (i.e., no menstrual bleeding for 12 months at a stretch). Bleeding during pregnancy and post-menopausal bleeding has different causes and needs immediate attention.
AUB is more common in teenagers or Premenopausal women. It may be due to structural abnormalities of the uterus, which may be benign (non-cancerous) like polyps, fibroids, adenomyosis (uterine thickening caused by endometrial tissue moving into the walls of the uterus) or malignant (cancerous). Other causes are:
- Lesions of the cervix and vagina (benign or malignant).
- Chronic infection of the endometrial lining (endometritis).
- Use of an Intrauterine device (IUD) or hormonal pills.
Hormonal disorders which affect cyclical ovulation (release of the egg from the ovary), namely Polycystic Ovarian Disease or other ovarian cysts, also cause AUB.
Diagnosis of the cause of AUB is done through a preliminary ultrasound of the pelvis (to rule out structural disorders) and some blood tests. Further investigations may be advised on preliminary test reports like Endometrial Biopsy, Hysteroscopy, CT or MRI of the pelvis.

Whatever be the cause of AUB, there are many treatment options available that can help resolve the problem. If there is no structural cause, medical treatment often helps restore the regular menstrual cycle. Structural causes are generally surgical entities and will require surgery like a myomectomy (removal of fibroid), cystectomy (removal of ovarian cysts), polyp removal and sometimes hysterectomy (removal of the uterus).
Dr Tejinder Kaur, DNB (OBG), MNAMS,Fellowship Reproductive Medicine
Practising in Chandigarh- Mohali- Zirakpur
Leave a Reply