There are several questions that may arise regarding the disease, but before answering, we need to fully understand what diabetes means

In today’s world, almost every household has a family member suffering from diabetes. There are several questions that may arise regarding the disease, but before answering those questions, we need to fully understand what diabetes means.
Diabetes is mainly considered a metabolic disorder, with the main presenting feature as hyperglycaemia, in other words, too much blood sugar in the bloodstream.
Prediabetes, or borderline diabetes, occurs when a person’s blood sugar levels are elevated but not enough for a diagnosis of diabetes. For a doctor to diagnose prediabetes, an individual must meet the criteria:
- glucose tolerance levels of 140–199 milligrams per decilitre (mg/dl)
- an HbA1C test result of 5.7–6.4%
- fasting blood sugar levels between 100–125 mg/dl
People living with prediabetes have a higher risk of developing type 2 diabetes, but they do not usually experience the symptoms of full diabetes.

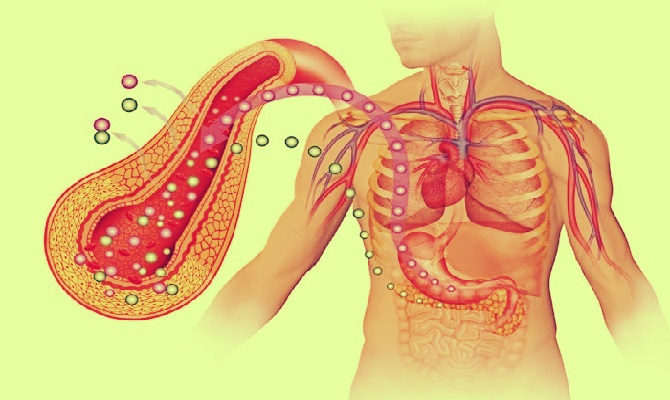
Role of Pancreas–
An important job of the pancreas is to produce insulin. This hormone controls the sugar in the blood by moving it into cells, where the body can use it for energy. In type 1 diabetes, which is relatively uncommon, the immune system attacks and destroys the cells in the pancreas that make insulin.
In type 2 diabetes, the pancreas makes insulin, but the cells don’t respond to it as they should. This is called insulin resistance. When glucose can’t get into cells, the blood sugar level rises. Then the pancreas works harder to make even more insulin.
Type of Diabetes–
There are two types of Diabetes, Type 1 and Type 2.
Type 1 diabetes, once known as juvenile diabetes or insulin-dependent diabetes, is a chronic condition. In this condition, the pancreas makes little or no insulin. Insulin is a hormone the body uses to allow sugar (glucose) to enter cells to produce energy.
In type 2 diabetes, there are primarily two interrelated problems at work. Your pancreas does not produce enough insulin — a hormone that regulates the movement of sugar into your cells — and cells respond poorly to insulin and take in less sugar
The risk factors for developing prediabetes and type 2 diabetes are similar. They include:
- being overweight
- a family history of diabetes
- having a high-density lipoprotein (HDL) cholesterol level lower than 40 mg/dl or 50 mg/dl
- a history of high blood pressure
- having gestational diabetes or giving birth to a child with a birth weight of more than 9 pounds
- a history of polycystic ovarian syndrome
- being of African American, Native American, Latin American, or Asian-Pacific Islander descent
- being more than 45 years of age
- having a sedentary lifestyle
Treatment and Management-
For managing Diabetes, the first line of treatment is lifestyle changes-
- Get moving with a fitness plan
- Follow a low-carb diet
- Cessation of smoking
- Watch your alcohol intake
- Managing stress
- Getting an annual blood work to check cholesterol, and blood pressure, an eye exam
The next treatment options for uncontrolled diabetes are medications. There are various classes of diabetic medicines, including insulin injections.
Health impact
Over time, diabetes can damage the heart, blood vessels, eyes, kidneys, and nerves.
Adults with diabetes have a two- to three-fold increased risk of heart attacks and strokes.
Combined with reduced blood flow, neuropathy (nerve damage) in the feet increases the chance of foot ulcers, infection, and the eventual need for limb amputation.
Diabetic retinopathy is a significant cause of blindness due to long-term accumulated damage to the small blood vessels in the retina. Close to 1 million people are blind due to diabetes.
Diabetes is among the leading causes of kidney failure
People with diabetes are more likely to have poor outcomes for several infectious diseases, including COVID-19.tes is among the leading causes of kidney failure
People with diabetes are more likely to have poor results for several contagious diseases, including COVID-19.

Leave a Reply